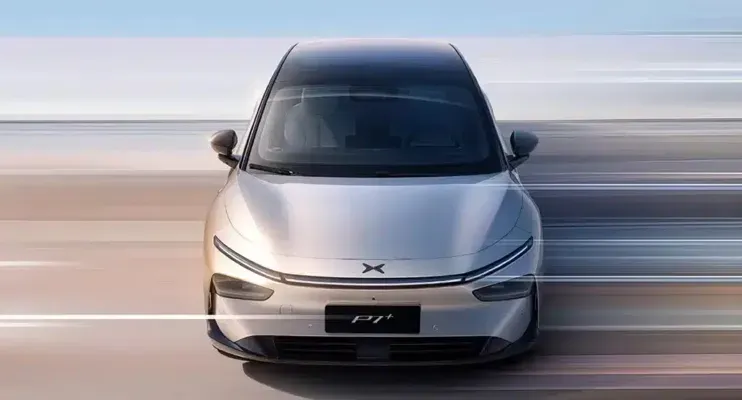
Xpeng’s autonomy approach is a bold stride into the future of self-driving technology, firmly distinguishing itself in the competitive landscape alongside industry giants like Tesla. With a pioneering commitment to a vision-based strategy, Xpeng has opted to forgo lidar, embracing advanced AI systems that utilize video data captured from its vehicles. This shift reflects a growing confidence in Xpeng’s Navigation Guided Pilot (XNGP), which offers a less controversial alternative to Tesla’s Full Self-Driving system. By leveraging AI in autonomous vehicles, Xpeng aims to provide seamless navigation capabilities that can adapt to the complex urban environments throughout China. As the debate between lidar vs camera systems continues, Xpeng’s innovative approach underscores the transformative potential of AI in redefining the future of mobility.
In the quest for true driving autonomy, Xpeng is redefining expectations with its innovative approach to self-navigation. The company’s shift away from traditional lidar technology towards a comprehensive, vision-based framework signifies a notable evolution in autonomous driving strategies. Rather than relying on complex sensor data, Xpeng is harnessing machine learning models that analyze real-time video inputs to enhance vehicle intelligence. This combination presents a fascinating challenge to existing paradigms dominated by competitors like Tesla, who still cling to more conventional navigation systems. As industry norms shift, Xpeng’s Navigation Guided Pilot stands out as a sophisticated alternative, matching the intensity of discussions around robotic taxis and AI-powered vehicles.
Xpeng’s Vision-Based Autonomy Strategy
Xpeng has taken a bold step in the realm of autonomous driving by fully embracing a vision-based strategy for its vehicles. This approach marks a significant shift from the initial reliance on Lidar, with senior director Candice Yuan asserting that Lidar data does not contribute effectively to their AI systems. Instead, Xpeng’s self-driving technology, known as Navigation Guided Pilot (XNGP), is predicated on integrating visual and linguistic data from real-world driving scenarios. With this method, Xpeng is aiming to create a more scalable solution that simplifies the AI learning process without the intricate demands of Lidar data integration.
The confidence in this vision-based model stems from extensive testing and real-time feedback from Xpeng’s fleet. By utilizing short videos captured from customer vehicles, Xpeng can train its AI to recognize and respond to a variety of driving situations. This strategy aligns with a growing consensus in the industry that robust video systems, coupled with advanced AI algorithms, can rival or surpass the interpretive capabilities offered by Lidar, particularly in urban environments where visual data is plentiful.
Comparative Analysis: Lidar vs Camera Systems in Autonomous Vehicles
The debate between Lidar and camera systems is pivotal in the realm of autonomous driving, fundamentally influencing the strategies adopted by various manufacturers. While Lidar has been praised for its ability to generate precise 3D maps of the vehicle’s surroundings, the high cost and complexity associated with Lidar systems pose significant challenges. In contrast, camera-centric approaches like those employed by Xpeng rely on straightforward, cost-effective hardware that can leverage existing video-based technologies to interpret scenes accurately. This makes them not only more accessible but also easier to implement across an expansive fleet.
However, it’s essential to recognize that each system has its strengths and drawbacks. Lidar excels in low-light conditions and can provide detailed distance measurements, making it invaluable in scenarios where visual cues may be lacking. Conversely, camera systems can elucidate more nuanced information about color, shape, and motion. Thus, while Xpeng has opted for a vision-based philosophy, companies like Waymo and Zoox demonstrate the enduring value of integrating diverse sensor technologies to enhance the overall robustness of autonomous systems.
The Evolution of Xpeng Navigation Guided Pilot (XNGP)
Xpeng’s Navigation Guided Pilot (XNGP) is a groundbreaking initiative aimed at streamlining the journey towards full autonomy. Unlike Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) approach, which is often surrounded by controversy due to its demand for driver intervention, XNGP presents a more pragmatic outlook on self-driving solutions. With a commitment focused on utilizing real-world driving data, Xpeng aims to equip its vehicles with capabilities to navigate varying environments across China. This strategic shift underscores a growing trend towards leveraging user-generated data for individualized learning experiences in vehicle autonomy.
The XNGP’s algorithm employs deep learning techniques and machine vision, allowing it to adapt to an array of driving conditions and scenarios. This adaptability is central to Xpeng’s vision for autonomy, as the company directly addresses the challenges of urban driving where complex interactions occur. By minimizing the reliance on Lidar, Xpeng is not only reducing costs but also enhancing its vehicles’ operational efficiency, propelling the brand forward in the crowded landscape of autonomous driving technology.
Xpeng’s Position in the Competitive Landscape of Self-Driving Technologies
In the rapidly evolving automotive landscape, Xpeng emerges as a significant player in the self-driving arena, strategically positioning itself against heavyweights like Tesla. By steering towards a vision-based autonomy paradigm, Xpeng captures attention not only for its technological approach but also for its competitive pricing and scalability. The essence of Xpeng’s strategy lies in developing an autonomous driving system that is both financially viable and user-friendly, distinguishing itself from competitors who may lean heavily on more expensive sensor technologies.
The interplay of Xpeng’s capabilities against Tesla’s FSD also introduces a variety of consumer perceptions and expectations regarding AI in autonomous vehicles. As Xpeng focuses on maximizing the functionality of cameras and integrated AIs, it challenges the narrative that only Lidar-equipped models can provide reliable self-driving experiences. This competition fuels innovation across the board, encouraging ongoing advancements in AI-driven solutions, while fostering a vibrant discourse about the best methodologies for achieving true vehicle autonomy.
The Future of AI in Autonomous Vehicles with Xpeng Leading the Way
Artificial intelligence is at the forefront of the evolution of autonomous vehicles, and Xpeng is positioning itself as a disruptor in this transformative journey. By prioritizing a vision-based system, Xpeng is not only simplifying the technological requirements associated with vehicle autonomy but also fostering a more flexible AI development environment. The AI infrastructure used by Xpeng emphasizes continuous learning and adaptation, rendering it particularly suitable for the dynamic traffic conditions and complexities encountered in China and beyond.
As the field of AI in autonomous vehicles expands, Xpeng’s commitment to harnessing advanced machine learning techniques will pave the way for more sophisticated self-driving capabilities. This innovation will ultimately lead to increased safety, efficiency, and user satisfaction as onboard systems become more adept at interpreting their surroundings in real-time. Moreover, as Xpeng refines its AI through customer interaction, the feedback loop generated is expected to drive improvements, setting a precedent for future autonomous vehicle designs industry-wide.
Implications of Xpeng’s Strategy on Global Autonomous Driving Standards
Xpeng’s shift to a vision-driven autonomy model may have significant implications for global standards in autonomous driving technology. By effectively demonstrating that a camera-centric approach can achieve similar or superior results compared to Lidar-based systems, Xpeng could influence other manufacturers to reconsider their technological dependencies. This evolution towards a more unified approach may encourage increased collaboration within the industry to establish shared benchmarks, ultimately enhancing both safety and performance across autonomous vehicles globally.
Furthermore, Xpeng’s developments could spark a new wave of regulatory frameworks aimed at harmonizing the evolution of self-driving technology. Clarity in standards will not only guide manufacturers but also shape public perceptions about the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles. Should Xpeng’s algorithms continue to prove effective, it could catalyze broader acceptance of non-Lidar-based systems, thereby reshaping consumer confidence and legislative approaches toward self-driving technologies across various markets.
Consumer Perception of Self-Driving Technologies: Xpeng vs Tesla
As Xpeng diverges from Tesla’s Lidar-dependent methods to embrace a vision-based framework, consumer perceptions around self-driving capabilities are being critically shaped. Despite Tesla’s pioneering position in autonomous technologies, concerns regarding the practical effectiveness of its Full Self-Driving system—dependent on consistent human oversight—continue to generate skepticism among potential users. This opens the door for Xpeng to polish its narrative, emphasizing the seamless integration of its XNGP system as a more intuitive alternative.
Consumer awareness and education are paramount as manufacturers like Xpeng strive to clarify the benefits of their proprietary technologies. By engaging directly with customers and presenting real-world use cases that illuminate the efficacy of camera-based systems, Xpeng can foster greater understanding and acceptance. In turn, as consumer trust builds around Xpeng’s autonomous solutions, the landscape of self-driving car ownership could witness a transformative shift, where users feel more confident entrusting their safety to technology.
Challenges Ahead for Xpeng in Achieving True Autonomy
Despite its significant strides, Xpeng faces substantial challenges as it continues its journey towards achieving true autonomy. Competing against established players like Tesla and other Lidar-utilizing companies requires relentless innovation and rigorous testing to refine its algorithms and systems. Additionally, Xpeng must navigate the intricate regulatory landscapes that shift constantly in response to advancements in technology and public safety concerns. Success in overcoming these obstacles will largely depend on the adaptability of Xpeng’s strategies.
Moreover, as Xpeng seeks to enhance its presence on the international stage, it must contend with other emerging technology trends and competitors in the autonomous driving space. The demand for high-level autonomy and the gradual transition towards greater acceptance will require Xpeng to continuously evolve and iterate on the foundational aspects of its Navigation Guided Pilot. Addressing these hurdles head-on is essential for Xpeng to maintain its competitive edge while achieving its ambitious goals in the world of autonomous vehicles.
Xpeng’s Collaborations and Partnerships in the Autonomous Vehicle Ecosystem
Xpeng’s approach to autonomy is complemented by strategic collaborations and partnerships that serve to enhance its technological infrastructure and market reach. By forming alliances with technology firms specializing in AI and machine vision, Xpeng can implement cutting-edge solutions that bolster the efficiency and safety of its self-driving systems. Such collaborations empower Xpeng to innovate rapidly while mitigating some of the inherent risks associated with developing new technologies independently.
Partnerships with academic institutions and AI research organizations also afford Xpeng unique insights and opportunities to explore new methodologies in vehicle autonomy. By engaging with thought leaders in the AI landscape, Xpeng can remain at the forefront of advancements that could reshape its autonomous driving capabilities. As the competition intensifies, leveraging external expertise through these partnerships will be crucial for Xpeng in achieving its vision of delivering a robust and reliable self-driving experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Xpeng’s approach to self-driving technology compared to Tesla’s?
Xpeng’s approach to self-driving, known as Navigation Guided Pilot (XNGP), focuses on a vision-based system that relies heavily on cameras and AI, contrasting with Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) that also incorporates similar technologies. Xpeng’s strategy emphasizes that lidar data is not integral to their AI’s performance, as they believe vision and language models can effectively handle driving tasks.
How does Xpeng utilize AI in its autonomous vehicles?
Xpeng leverages AI in its autonomous vehicles through its unique VLA model—Vision, Language, and Action. This model is primarily trained on short videos captured from customer vehicles, enabling the self-driving system to interpret surroundings and make decisions based on visual data without the need for lidar.
What are the benefits of Xpeng’s navigation approach over lidar systems?
Xpeng’s navigation approach offers advantages such as reduced costs and complexity. By eliminating lidar from its vehicles, Xpeng simplifies its AI training process, utilizing video data which can be more straightforward to integrate into machine learning models compared to the extensive requirements of lidar data.
Why has Xpeng removed lidar from its autonomous vehicle technology?
Xpeng removed lidar from its autonomous vehicle technology because they found that lidar data could not significantly enhance their AI system. Senior director Candice Yuan noted that their vision-based AI could function effectively without lidar, focusing instead on training models using visual data from customer vehicles.
How does Xpeng’s autonomous driving technology compare to other autonomous taxi companies?
Compared to companies like Waymo and Zoox, which utilize lidar for their AI training, Xpeng’s focus is on a camera-based system that employs machine learning with visual data. While Waymo offers extensive fully driverless rides, Xpeng’s Navigation Guided Pilot still requires driver supervision, positioning it differently in the autonomous driving landscape.
Is Xpeng’s Navigation Guided Pilot truly autonomous?
While Xpeng’s Navigation Guided Pilot (XNGP) aims for a high level of autonomy, it still necessitates driver oversight, similar to Tesla’s systems. The company claims its AI can navigate various conditions in China theoretically, though it has yet to achieve true self-driving without human intervention, contrasting with fully autonomous systems like Waymo.
What challenges does Xpeng face in the implementation of its vision-based autonomous system?
Xpeng faces challenges in ensuring that its vision-based autonomous system can handle diverse driving conditions effectively. While operating without lidar simplifies technology costs, the system must be robust enough to interpret complex environments, particularly in adverse conditions that might typically benefit from lidar data.
What role do cameras play in Xpeng’s autonomy strategy?
Cameras are central to Xpeng’s autonomy strategy, serving as the primary sensors for their Navigation Guided Pilot system. The reliance on cameras aligns with their belief in the effectiveness of video data for training their AI models, allowing them to interpret and respond to real-world driving scenarios appropriately.