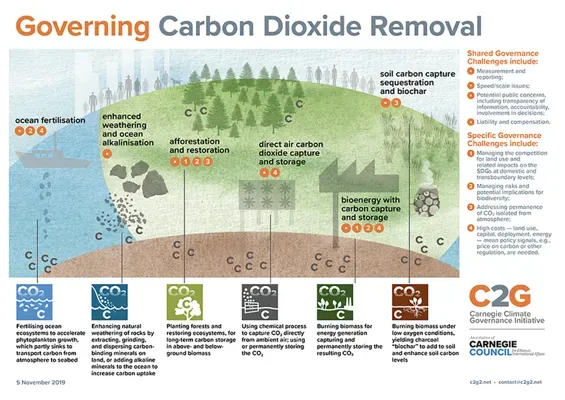
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) is increasingly becoming a focal point in the race against climate change, especially as corporations strive to meet net-zero emissions targets. As defined by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, effective CDR methods are essential for mitigating climate pollution and ensuring a sustainable future. However, recent findings suggest that many businesses are misusing temporary solutions like tree-planting instead of investing in more durable carbon removal strategies that genuinely address the challenge. This dissonance raises significant environmental risks, prompting the need for greater scrutiny of corporate climate claims. The urgency of adopting reliable CDR techniques emphasizes the importance of holding companies accountable for their contributions to climate stability.
The conversation surrounding climate mitigation has expanded to include various alternative terms synonymous with carbon dioxide removal, such as carbon capture technology and greenhouse gas elimination. With the rising emphasis on achieving emissions neutrality, firms are increasingly recognized for their efforts in climate action through mechanisms like sequestration or CO2 elimination from the atmosphere. Although some corporations make claims about offsetting their environmental footprint, many fail to prioritize sustainable and durable methods, relying instead on short-term carbon offsets. This trend illuminates the need for cohesive strategies that drive both accountability and effective solutions in tackling atmospheric CO2 levels. By adopting a broader lexicon in discussions of ecological stewardship, we can foster a more comprehensive understanding of the pathways to effective climate action.
The Importance of Carbon Dioxide Removal in Achieving Net-Zero Emissions
The role of carbon dioxide removal (CDR) is pivotal in the global fight against climate change, especially in achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. As temperatures rise due to increased greenhouse gas emissions, the urgency to implement effective CDR technologies has never been more critical. Organizations like the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change highlight that while reducing emissions is fundamental, actively removing CO2 from the atmosphere is essential to curb the impacts of climate pollution. Companies that neglect to prioritize durable CDR in their strategies risk falling short of their environmental responsibilities and misrepresenting their commitment to sustainability.
However, a troubling trend has emerged where large corporations are heavily investing in short-term and less effective forms of CDR, such as tree planting, while largely ignoring the more reliable and durable CDR methods needed for long-term climate mitigation. This misalignment between corporate climate claims and the actual efficacy of carbon removal strategies can create significant environmental risks and undermine progress towards net-zero targets. Clearly defining what constitutes durable carbon removal and encouraging sustainable practices across sectors is imperative for both corporate credibility and environmental protection.
Corporate Climate Claims vs. Reality: The Truth About CDR Investments
The stark contrast between corporate climate claims and the reality of their actions regarding carbon dioxide removal reveals significant gaps in accountability. Many large corporations are quick to promote their climate initiatives yet often invest in nonsustainable methods that offer superficial solutions to their emissions problems. According to the NewClimate Institute’s report, companies like DTE Energy are using these non-durable methods for their net-zero claims, which are unsustainable and do not contribute to long-term carbon capture. This discrepancy not only misleads consumers and stakeholders but also damages the overall credibility of climate action efforts.
Moreover, substantial investments are often diverted towards carbon capture and storage technologies, which might capture emissions at their source but do little to reduce atmospheric CO2 levels overall. Without a shift towards investing in durable CDR, which could effectively sequester carbon for millennia, companies will continue to perpetuate a cycle of climate pollution and inadequate responses. Transparency in reporting emissions and the effectiveness of CDR investments is crucial to holding corporations accountable and ensuring they fulfill their climate promises.
The Role of Government in Scaling Up Durable Carbon Removal Technologies
Government action is essential for scaling up durable carbon removal technologies and ensuring accountability among corporations. Many experts believe that the next decade is crucial for developing and deploying effective CDR solutions that can withstand scrutiny and deliver real climate benefits. Governments should establish clear regulations and funding mechanisms to support the research and development of durable CDR, as well as incentivize companies to invest responsibly. By prioritizing regulatory frameworks, governments can mitigate risks associated with climate pollution and drive industries towards more sustainable practices.
Additionally, governments can enhance corporate transparency by requiring businesses to publicly disclose their CDR investments and their long-term impacts on reducing emissions. This level of scrutiny can foster competition while prompting companies to prioritize genuine emissions reductions over temporary offsets. Engaging the private sector in meaningful dialogue about environmental risk and sustainable practices is vital for advancing the global climate agenda and building a robust infrastructure around durable CDR.
The Future of CDR: Innovative Approaches and Sustainable Solutions
As we look to the future, innovative approaches to carbon dioxide removal are continuously emerging. Technologies that can capture CO2 efficiently and store it for centuries are becoming the focus of research initiatives aimed at enhancing durability and scalability. Solutions such as direct air capture and bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) represent promising pathways to not only removing atmospheric CO2 but also integrating renewable energy sources into the process. Emphasizing innovation will be critical in shifting the focus from mere emissions offsets to sustainable, long-term CDR solutions.
Moreover, a collaborative approach involving cross-sector partnerships can drive the development of effective CDR technologies. By pooling resources and expertise, corporations can explore cutting-edge strategies that align with their net-zero commitments while benefiting the broader community and ecosystem. This cooperative environment will foster the advancement of sustainable practices and ultimately contribute to a more resilient global response to climate change.
Understanding Durable Carbon Removal: Methods and Misconceptions
Durable carbon removal encompasses a range of methods that ensure captured CO2 is sequestered for long periods, significantly reducing atmospheric concentrations. Techniques such as mineralization, where CO2 is transformed into stable carbonates, are examples of enduring solutions that can mitigate environmental risks associated with climate change. In contrast, many corporate claims often conflate these long-term methods with temporary solutions that fail to deliver meaningful results. Understanding the differences between durable and nondurable carbon removal methods is crucial for corporations aiming to build credible climate action plans.
Furthermore, educational efforts focusing on what constitutes durable CDR can help dismantle prevalent misconceptions within the corporate sector. Businesses need to understand that investing in quick fixes, such as planting trees, while neglecting permanent solutions undermines their long-term sustainability goals. By emphasizing the importance of durable methods, organizations can better align their environmental initiatives with scientifically supported practices that truly contribute to combatting climate pollution.
Corporate Accountability: The Need for Transparency in CDR Investments
Corporate accountability is essential for ensuring that companies not only make ambitious climate pledges but also follow through with actions that align with their commitments. Transparency regarding investments in carbon dioxide removal technologies is critical. It allows consumers, investors, and regulatory bodies to gauge the effectiveness of corporate strategies in combating climate change. Without clear disclosure mechanisms, businesses risk undermining public trust and diverting attention from the pressing need for genuine emissions reductions.
Establishing stringent reporting standards for companies’ CDR investments can facilitate more accurate assessments of their environmental impact. By being open about both the benefits and limitations of their CDR strategies, companies can build credibility and inspire confidence among stakeholders. Moreover, this transparency is vital for driving sector-wide adoption of durable carbon removal techniques that effectively combat climate pollution.
Short-Term Gains vs. Long-Term Climate Commitment: A Critical Examination
The tension between short-term gains and long-term commitments in corporate climate strategies often leads to a reliance on ineffective carbon removal methods. Many companies are focused on achieving immediate targets without considering the long-term implications of their actions. This myopic view disregards the fact that sustainable success in mitigating climate change hinges on investing in durable carbon removal. Short-term offsets may stabilize emissions temporarily, but they do not equate to genuine progress towards a net-zero future.
In critically evaluating corporate climate commitments, it becomes evident that reliance on non-durable CDR methods can create false narratives about progress. Companies that prioritize short-term solutions over long-lasting ones divert attention away from vital emissions reductions and potentially put their reputations at risk. It is essential for organizations to commit sincerely to long-term strategies that will effectively address climate risks and align with global sustainability goals.
The Impact of Technology on Sustainable CDR Practices
Technological advancements play a significant role in the evolution of sustainable carbon dioxide removal practices. Innovations in carbon capture technologies, such as direct air capture systems, are making it more feasible to implement durable CDR solutions at scale. These advancements not only enhance the efficiency of CO2 removal but also provide new pathways for integrating sustainable energy sources, such as wind and solar, into carbon management strategies. As technology evolves, businesses must stay informed and invest in solutions that prioritize longevity and practicality.
Furthermore, collaboration between technology developers and corporations can catalyze breakthroughs in durable CDR methods. By fostering partnerships that bring together researchers, engineers, and industry leaders, companies can access cutting-edge innovations that could redefine how carbon is removed from the atmosphere. Emphasizing technology will meet the urgent demands of climate change and support the development of scalable and effective carbon removal solutions.
Navigating Corporate Climate Risks: Lessons Learned from CDR Practices
As corporations navigate the complexities of their climate commitments, it has become increasingly important to learn from past practices related to carbon dioxide removal. Many businesses have fallen into the trap of relying on quick fixes, which often lead to ineffective climate strategies and a lack of genuine progress. By analyzing these past challenges, companies can better understand the potential environmental risks of certain CDR methods and make informed decisions that prioritize sustainability.
The importance of mitigating environmental risks associated with CDR is clear, as seen in the NewClimate Institute’s findings. Companies must take a proactive approach to assess the impacts of their CDR investments on biodiversity, renewable energy demand, and long-term sustainability. Adopting a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between corporate actions and environmental outcomes will enable businesses to establish effective, transparent, and credible climate strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is carbon dioxide removal (CDR) and why is it important for achieving net-zero emissions?
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) refers to the processes and technologies that capture and store CO2 from the atmosphere, helping to counteract climate pollution. Achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, as outlined by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, requires effective CDR methods that can offset remaining emissions after significant reductions are made.
What are the different types of carbon dioxide removal methods and which are considered durable?
CDR methods vary, with examples including tree planting and soil carbon storage, which are considered nondurable due to their short-term effectiveness. Durable carbon removal techniques include geological carbon storage and mineralization, which can safely lock away CO2 for at least 1,000 years, making them essential for long-term climate strategies.
How do corporate climate claims relate to carbon dioxide removal?
Many corporations are making climate claims based on short-term carbon dioxide removal methods, such as tree planting, which may not contribute meaningfully to long-term net-zero emissions goals. There’s a critical need for businesses to invest in durable carbon removal technologies that align with genuine emissions reductions.
Why is there a mismatch between corporate climate claims and effective carbon dioxide removal practices?
The NewClimate Institute’s report highlights that while many corporations claim to offset their climate pollution through CDR, they often invest in short-lived methods rather than durable solutions, creating a dangerous discrepancy in their actual climate impact versus their public commitments.
What role does the government play in supporting durable carbon dioxide removal projects?
Government investment and regulations are crucial for scaling up durable carbon dioxide removal technologies. As experts deem the next decade critical for development in this field, public sector support can help ensure that effective CDR solutions are implemented alongside comprehensive emissions reduction strategies.
How do different industries approach carbon dioxide removal and its impact on their climate strategies?
Among various sectors, technology companies lead in investing in durable CDR, while sectors like aviation and fossil fuels show varying degrees of commitment. Many companies rely on immediate carbon capture solutions without reducing their emissions significantly, which reflects a need for stronger accountability in corporate climate strategies.
What challenges exist for the scalability of durable carbon dioxide removal methods?
Currently, durable carbon dioxide removal methods are not widely scalable, with such techniques making up only about 0.1% of global carbon removal annually. This limitation, along with high costs and development barriers, hinders broader adoption and effectiveness in achieving net-zero emissions.
Why is transparency in carbon dioxide removal projects important for corporations?
Transparency is vital in carbon dioxide removal projects to inform stakeholders about potential environmental and social risks. Without clear disclosures, there is a risk that companies may misrepresent their contributions to climate goals, undermining the credibility of their climate commitments.
How can companies improve their approach to carbon dioxide removal?
Companies should prioritize genuine emissions reductions over reliance on carbon dioxide removal as a mere offset. Emphasizing investments in durable CDR technologies and transparent reporting practices can enhance the integrity of corporate climate actions and better support global net-zero targets.
What recommendations does the NewClimate Institute provide for effective carbon dioxide removal practices?
The NewClimate Institute suggests that companies clarify what constitutes durable carbon removal, establish distinct emissions reduction targets separate from CDR contributions, and prioritize mitigation efforts over offsetting strategies to ensure substantive progress towards climate goals.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Need for Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) | Essential to counteract greenhouse gas emissions and limit global warming, as emphasized by the IPCC. |
| Corporate Investment in CDR | Major companies are focusing on short-term solutions like tree planting rather than effective, durable CDR methods. |
| Durable vs. Nondurable CDR | Durable CDR involves long-lasting methods like geological injection, while nondurable methods can only hold carbon for a limited time. |
| Current Challenges | Scale-up of durable CDR methods is hindered by lack of investment and regulatory support. |
| Corporate Responsibility | Companies should prioritize emissions reduction over relying on CDR projects for climate targets. |
| Future Governance | Proper regulation of CDR and corporate claims is crucial and likely requires government intervention. |
Summary
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) is an essential strategy in combating climate change and achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. However, recent findings indicate that many large corporations are not investing in the most effective forms of CDR, opting instead for less sustainable alternatives. To genuinely make progress in reducing atmospheric CO2 levels, it is crucial for companies to align their strategies with durable CDR solutions and prioritize emission reductions over offsets. Enhanced government regulations and clear accountability are needed to ensure that corporate commitments to CDR aren’t merely superficial but drive significant climate action.